Travel Journals
What improves access to primary healthcare services in rural communities? A systematic review | BMC Primary Care
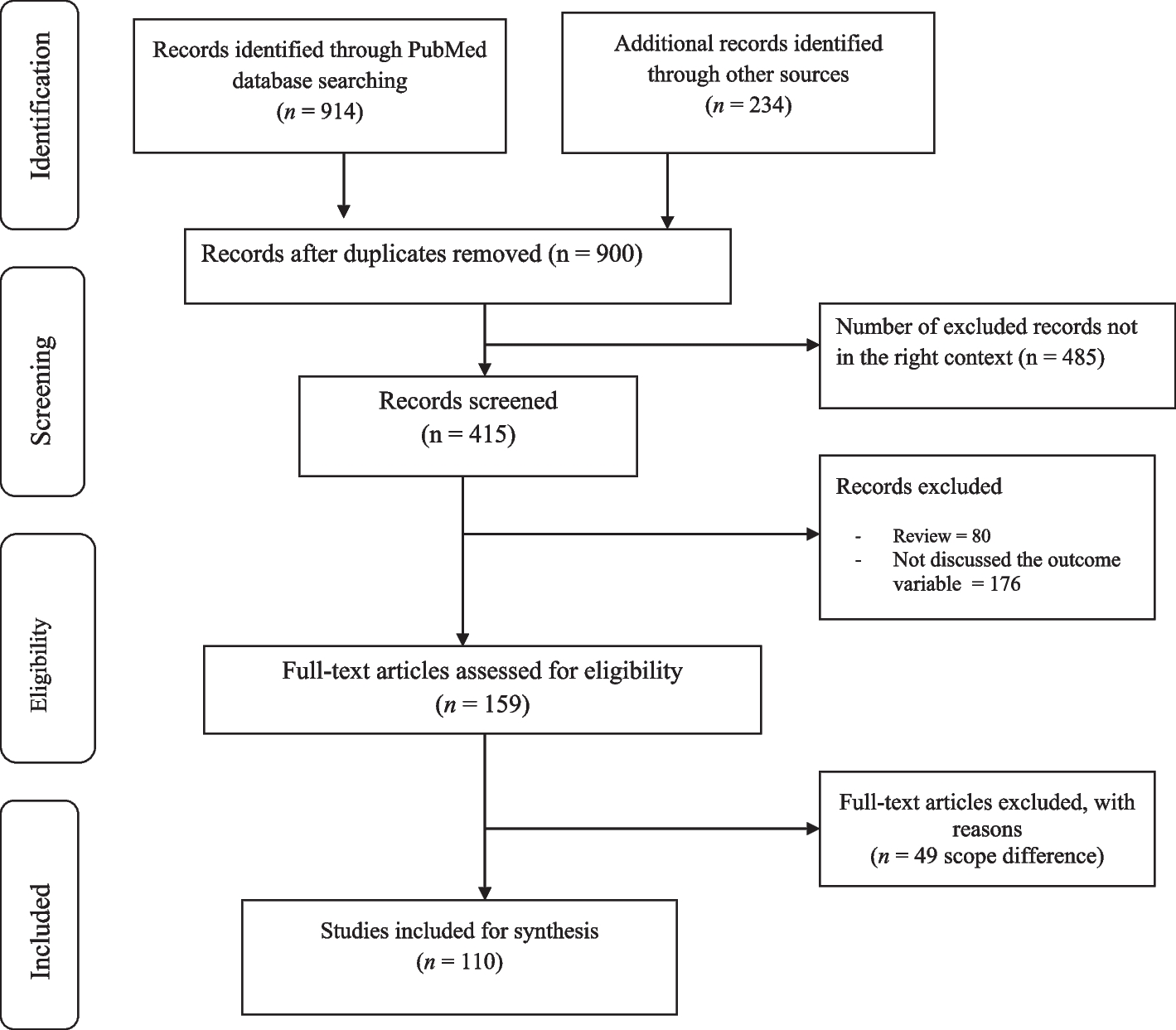
Hampton MB, Kettle AJ, Winterbourn CC. Inside the neutrophil phagosome: oxidants, myeloperoxidase, and bacterial killing. Blood. 1998;92(9):3007–17.
Kirby M. The right to health fifty years on: Still skeptical? Health Hum Rights. 1999;4(1):6–25.
O’Connell T, Rasanathan K, Chopra M. What does universal health coverage mean? The Lancet. 2014;383(9913):277–9.
White F. Primary health care and public health: foundations of universal health systems. Med Princ Pract. 2015;24(2):103–16.
Sanders D, Nandi S, Labonté R, Vance C, Van Damme W. From primary health care to universal health coverage—one step forward and two steps back. The Lancet. 2019;394(10199):619–21.
Brezzi M, Luongo P. Regional Disparities In Access To Health Care. 2016.
Hartley D. Rural health disparities, population health, and rural culture. Am J Public Health. 2004;94(10):1675–8.
Walraven G. The 2018 Astana declaration on primary health care, is it useful? J Glob Health. 2019;9(1).
Gillam S. Is the declaration of Alma Ata still relevant to primary health care? BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2008;336(7643):536–8.
Tollman S, Doherty J, Mulligan JA. General Primary Care. In: Jamison DT, Breman JG, Measham AR, Alleyne G, Claeson M, Evans DB, Jha P, Mills A, Musgrove P, editors. Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries. Washington: World Bank The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank Group; 2006. Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK11789/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK11789.pdf.
Stern C, Jordan Z, McArthur A. Developing the review question and inclusion criteria. AJN The Am J Nurs. 2014;114(4):53–6.
World Health Organization. losing the gap in a generation. Commission on Social Determinants of Health FINAL REPORT. 2008. Available at https://www.who.int/social_determinants/final_report/csdh_finalreport_2008.pdf. Accessed on 22 March 2022.
Hong QN, Pluye P, Fàbregues S, Bartlett G, Boardman F, Cargo M, Dagenais P, GagnonM-P GF, Nicolau B, O’Cathain A. Mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT), version 2018. Canada: IC Canadian Intellectual Property Office, Industry; 2018. Available at https://mixedmethodsappraisaltoolpublicpbworks.com/w/file/fetch/127916259/MMAT_2018_criteria-manual_2018-08-01_ENG.pdf.
JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. Appendix 8.1 JBI Mixed Methods Data Extraction Form following a Convergent Integrated Approach. Available at https://jbi-global-wiki.refined.site/space/MANUAL/3318284375/Appendix+8.1+JBI+Mixed+Methods+Data+Extraction+Form+following+a+Convergent+Integrated+Approach. Accessed on 12 August 2021.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097.
Assefa Y, Gelaw YA, Hill PS, Taye BW, Van Damme W. Community health extension program of Ethiopia, 2003–2018: successes and challenges toward universal coverage for primary healthcare services. Glob Health. 2019;15(1):1–11.
Admassie A, Abebaw D, Woldemichael AD. Impact evaluation of the Ethiopian health services extension programme. J Dev Eff. 2009;1(4):430–49.
Yitayal M, Berhane Y, Worku A, Kebede Y. The community-based Health extension Program significantly improved contraceptive utilization in West gojjam Zone, ethiopia. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2014;7:201.
Croke K, Mengistu AT, O’Connell SD, Tafere K. The impact of a health facility construction campaign on health service utilisation and outcomes: analysis of spatially linked survey and facility location data in Ethiopia. BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(8):e002430.
Arwal S. Health Posts in Afghanistan. J Gen Practice. 2015;3(213):2.
Negussie A, Girma G. Is the role of Health Extension Workers in the delivery of maternal and child health care services a significant attribute? The case of Dale district, southern Ethiopia. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):1–8.
Than KK, Mohamed Y, Oliver V, Myint T, La T, Beeson JG, Luchters S. Prevention of postpartum haemorrhage by community-based auxiliary midwives in hard-to-reach areas of Myanmar: a qualitative inquiry into acceptability and feasibility of task shifting. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17(1):1–10.
Medhanyie A, Spigt M, Kifle Y, Schaay N, Sanders D, Blanco R, GeertJan D, Berhane Y. The role of health extension workers in improving utilization of maternal health services in rural areas in Ethiopia: a cross sectional study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012;12(1):1–9.
Sakeah E, McCloskey L, Bernstein J, Yeboah-Antwi K, Mills S, Doctor HV. Can community health officer-midwives effectively integrate skilled birth attendance in the community-based health planning and services program in rural Ghana? Reprod Health. 2014;11(1):1–13.
Sarmento DR. Traditional birth attendance (TBA) in a health system: what are the roles, benefits and challenges: a case study of incorporated TBA in Timor-Leste. Asia Pac Fam Med. 2014;13(1):1–9.
Rahmawati R, Bajorek B. Peer Reviewed: A Community Health Worker-Based Program for Elderly People with Hypertension in Indonesia: A Qualitative Study, 2013. Prev Chronic Dis. 2015;12:E175.
Feltner FJ, Ely GE, Whitler ET, Gross D, Dignan M. Effectiveness of community health workers in providing outreach and education for colorectal cancer screening in Appalachian Kentucky. Soc Work Health Care. 2012;51(5):430–40.
Hughes MM, Yang E, Ramanathan D, Benjamins MR. Community-based diabetes community health worker intervention in an underserved Chicago population. J Community Health. 2016;41(6):1249–56.
Panday S, Bissell P, Van Teijlingen E, Simkhada P. The contribution of female community health volunteers (FCHVs) to maternity care in Nepal: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):1–11.
Datiko DG, Lindtjørn B. Health extension workers improve tuberculosis case detection and treatment success in southern Ethiopia: a community randomized trial. PLoS ONE. 2009;4(5):e5443.
le Roux KW, Almirol E, Rezvan PH, Le Roux IM, Mbewu N, Dippenaar E, Stansert-Katzen L, Baker V, Tomlinson M, Rotheram-Borus M. Community health workers impact on maternal and child health outcomes in rural South Africa–a non-randomized two-group comparison study. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1–14.
Witmer A, Seifer SD, Finocchio L, Leslie J, O’Neil EH. Community health workers: integral members of the health care work force. Am J Public Health. 1995;85(8 Pt 1):1055–8.
Wright RA. Community-oriented primary care. The cornerstone of health care reform. Jama. 1993;269(19):2544–7.
Makaula P, Bloch P, Banda HT, Mbera GB, Mangani C, de Sousa A, Nkhono E, Jemu S, Muula AS. Primary Health Care in rural Malawi – a qualitative assessment exploring the relevance of the community-directed interventions approach. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012;12:328.
Katabarwa MN, Habomugisha P, Richards FO Jr, Hopkins D. Community-directed interventions strategy enhances efficient and effective integration of health care delivery and development activities in rural disadvantaged communities of Uganda. Trop Med Int Health : TM & IH. 2005;10(4):312–21.
Madon S, Malecela MN, Mashoto K, Donohue R, Mubyazi G, Michael E. The role of community participation for sustainable integrated neglected tropical diseases and water, sanitation and hygiene intervention programs: A pilot project in Tanzania. Soc Sci Med. 1982;2018(202):28–37.
Okeibunor JC, Orji BC, Brieger W, Ishola G, Otolorin E, Rawlins B, Ndekhedehe EU, Onyeneho N, Fink G. Preventing malaria in pregnancy through community-directed interventions: evidence from Akwa Ibom State, Nigeria. Malaria J. 2011;10:227.
Brieger WR, Sommerfeld JU, Amazigo UV. The Potential for Community-Directed Interventions: Reaching Underserved Populations in Africa. Int Q Community Health Educ. 2015;35(4):295–316.
Braimah JA, Sano Y, Atuoye KN, Luginaah I. Access to primary health care among women: the role of Ghana’s community-based health planning and services policy. Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2019;20:e82.
Kaplan DW, Brindis CD, Phibbs SL, Melinkovich P, Naylor K, Ahlstrand K. A comparison study of an elementary school–based health center: effects on health care access and use. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153(3):235–43.
Allison MA, Crane LA, Beaty BL, Davidson AJ, Melinkovich P, Kempe A. School-based health centers: improving access and quality of care for low-income adolescents. Pediatrics. 2007;120(4):e887–94.
Keeton V, Soleimanpour S, Brindis CD. School-based health centers in an era of health care reform: Building on history. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2012;42(6):132–56.
Brindis CD, Klein J, Schlitt J, Santelli J, Juszczak L, Nystrom RJ. School-based health centers: Accessibility and accountability. J Adolesc Health. 2003;32(6):98–107.
Hutchinson P, Carton TW, Broussard M, Brown L, Chrestman S. Improving adolescent health through school-based health centers in post-Katrina New Orleans. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2012;34(2):360–8.
Paschall MJ, Bersamin M. School-based health centers, depression, and suicide risk among adolescents. Am J Prev Med. 2018;54(1):44–50.
Minguez M, Santelli JS, Gibson E, Orr M, Samant S. Reproductive health impact of a school health center. J Adolesc Health. 2015;56(3):338–44.
Gibson EJ, Santelli JS, Minguez M, Lord A, Schuyler AC. Measuring school health center impact on access to and quality of primary care. J Adolesc Health. 2013;53(6):699–705.
Bozigar M. A Cross-Sectional Survey to Evaluate Potential for Partnering With School Nurses to Promote Human Papillomavirus Vaccination. Prev Chronic Dis. 2020;17:E111.
Suen J, Attrill S, Thomas JM, Smale M, Delaney CL, Miller MD. Effect of student-led health interventions on patient outcomes for those with cardiovascular disease or cardiovascular disease risk factors: a systematic review. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020;20(1):1–10.
Atuyambe LM, Baingana RK, Kibira SP, Katahoire A, Okello E, Mafigiri DK, Ayebare F, Oboke H, Acio C, Muggaga K. Undergraduate students’ contributions to health service delivery through communitybased education. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:123.
Stuhlmiller CM, Tolchard B. Developing a student-led health and wellbeing clinic in an underserved community: collaborative learning, health outcomes and cost savings. BMC Nurs. 2015;14(1):1–8.
Campbell DJ, Gibson K, O’Neill BG, Thurston WE. The role of a student-run clinic in providing primary care for Calgary’s homeless populations: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13(1):1–6.
Simpson SA, Long JA. Medical student-run health clinics: important contributors to patient care and medical education. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22(3):352–6.
Gruen RL, O’Rourke IC, Bailie RS, d’Abbs PH, O’Brien MM, Verma N. Improving access to specialist care for remote Aboriginal communities: evaluation of a specialist outreach service. Med J Aust. 2001;174(10):507–11.
Gruen RL, Weeramanthri T, Bailie R. Outreach and improved access to specialist services for indigenous people in remote Australia: the requirements for sustainability. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2002;56(7):517–21.
Gruen RL, Bailie RS, Wang Z, Heard S, O’Rourke IC. Specialist outreach to isolated and disadvantaged communities: a population-based study. The Lancet. 2006;368(9530):130–8.
Bond M, Bowling A, Abery A, McClay M, Dickinson E. Evaluation of outreach clinics held by specialists in general practice in England. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2000;54(2):149–56.
Irani M, Dixon M, Dean JD. Care closer to home: past mistakes, future opportunities. J R Soc Med. 2007;100(2):75–7.
Bailey JJ, Black ME, Wilkin D. Specialist outreach clinics in general practice. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 1994;308(6936):1083–6.
De Roodenbeke E, Lucas S, Rouzaut A, Bana F. Outreach services as a strategy to increase access to health workers in remote and rural areas. Geneva: WHO; 2011.
Bowling A, Stramer K, Dickinson E, Windsor J, Bond M. Evaluation of specialists’ outreach clinics in general practice in England: process and acceptability to patients, specialists, and general practitioners. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1997;51(1):52–61.
Spencer N. Consultant paediatric outreach clinics–a practical step in integration. Arch Dis Child. 1993;68(4):496–500.
Aljasir B, Alghamdi MS. Patient satisfaction with mobile clinic services in a remote rural area of Saudi Arabia. East Mediterr Health J. 2010;16(10):1085–90.
Lee EJ, O’Neal S. A mobile clinic experience: nurse practitioners providing care to a rural population. J Pediatr Health Care. 1994;8(1):12–7.
Cone PH, Haley JM. Mobile clinics in Haiti, part 1: Preparing for service-learning. Nurse Educ Pract. 2016;21:1–8.
Diaz-Perez Mde J, Farley T, Cabanis CM. A program to improve access to health care among Mexican immigrants in rural Colorado. J Rural Health. 2004;20(3):258–64.
Hill C, Zurakowski D, Bennet J, Walker-White R, Osman JL, Quarles A, Oriol N. Knowledgeable Neighbors: a mobile clinic model for disease prevention and screening in underserved communities. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(3):406–10.
Edgerley LP, El-Sayed YY, Druzin ML, Kiernan M, Daniels KI. Use of a community mobile health van to increase early access to prenatal care. Matern Child Health J. 2007;11(3):235–9.
Peters G, Doctor H, Afenyadu G, Findley S, Ager A. Mobile clinic services to serve rural populations in Katsina State, Nigeria: perceptions of services and patterns of utilization. Health Policy Plan. 2014;29(5):642–9.
Neke NM, Gadau G, Wasem J. Policy makers’ perspective on the provision of maternal health services via mobile health clinics in Tanzania—Findings from key informant interviews. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(9):e0203588.
Padmadas SS, Johnson FA, Leone T, Dahal GP. Do mobile family planning clinics facilitate vasectomy use in Nepal? Contraception. 2014;89(6):557–63.
Macinko J, Harris MJ. Brazil’s family health strategy—delivering community-based primary care in a universal health system. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(23):2177–81.
Macinko J, Lima Costa MF. Access to, use of and satisfaction with health services among adults enrolled in Brazil’s Family Health Strategy: evidence from the 2008 National Household Survey. Tropical Med Int Health. 2012;17(1):36–42.
Dourado I, Oliveira VB, Aquino R, Bonolo P, Lima-Costa MF, Medina MG, Mota E, Turci MA, Macinko J. Trends in primary health care-sensitive conditions in Brazil: the role of the Family Health Program (Project ICSAP-Brazil). Medical care. 2011;49:577–84.
Aquino R, De Oliveira NF, Barreto ML. Impact of the family health program on infant mortality in Brazilian municipalities. Am J Public Health. 2009;99(1):87–93.
Chong P-N, Tang WE. Transforming primary care—the way forward with the TEAMS2 approach. Fam Pract. 2019;36(3):369–70.
Primary Health Care Performance Initiatives (phcpi). Improvement strategies model: Population health management: Empanelment. Available at https://improvingphc.org/sites/default/files/Empanelment%20-%20v1.2%20-%20last%20updated%2012.13.2019.pdf. Accessed on 18 March 2022.
McGough P, Chaudhari V, El-Attar S, Yung P. A health system’s journey toward better population health through empanelment and panel management. Healthcare. 2018;6(66):1–9.
Bearden T, Ratcliffe HL, Sugarman JR, Bitton A, Anaman LA, Buckle G, Cham M, Quan DCW, Ismail F, Jargalsaikhan B. Empanelment: A foundational component of primary health care. Gates Open Res. 2019;3:1654.
Hsiao WC. Unmet health needs of two billion: is community financing a solution? 2001.
Wang W, Temsah G, Mallick L. The impact of health insurance on maternal health care utilization: evidence from Ghana, Indonesia and Rwanda. Health Policy Plan. 2017;32(3):366–75.
Atnafu DD, Tilahun H, Alemu YM. Community-based health insurance and healthcare service utilisation, North-West, Ethiopia: a comparative, cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2018;8(8):e019613.
USAID. Ethiopia’s Community-based Health Insurance: A Step on the Road to Universal Health Coverage. Available at https://www.hfgproject.org/ethiopias-community-based-health-insurance-step-road-universal-health-coverage/. Accessed on 18 March 2022.
Blanchet NJ, Fink G, Osei-Akoto I. The effect of Ghana’s National Health Insurance Scheme on health care utilisation. Ghana Med J. 2012;46(2):76–84.
Nshakira-Rukundo E, Mussa EC, Nshakira N, Gerber N, von Braun J. Impact of community-based health insurance on utilisation of preventive health services in rural Uganda: a propensity score matching approach. Int J Health Econ Manag. 2021;21(2):203–27.
Mwaura JW, Pongpanich S. Access to health care: the role of a community based health insurance in Kenya. Pan Afr Med J. 2012;12(1):35.
Jutting JP. The Impact Of Health Insurance On The Access To Health Care And Financial Protection In Rural Developing Countries: The Example of Senegal. HNP discussion paper series;. World Bank, Washington, DC. © World Bank. 2011. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/13774. License: CC BY 3.0 IGO.
Balamiento NC. The impact of social health insurance on healthcare utilization outcomes: evidence from the indigent program of the Philippine National Health Insurance. International Institute of Social Studies. 2018. Available at https://thesis.eur.nl/pub/46445/Balamiento,%20Neeanne_MA_2017_18%20_ECD.pdf. Accessed 30 Nov 2022.
Farrell CM, Gottlieb A. The effect of health insurance on health care utilization in the justice-involved population: United States, 2014–2016. Am J Public Health. 2020;110(S1):S78–84.
Thuong NTT. Impact of health insurance on healthcare utilisation patterns in Vietnam: a survey-based analysis with propensity score matching method. BMJ Open. 2020;10(10):e040062.
Custodio R, Gard AM, Graham G. Health information technology: addressing health disparity by improving quality, increasing access, and developing workforce. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2009;20(2):301–7.
Meier CA, Fitzgerald MC, Smith JM. eHealth: extending, enhancing, and evolving health care. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2013;15:359–82.
Anstey Watkins JOT, Goudge J, Gomez-Olive FX, Griffiths F. Mobile phone use among patients and health workers to enhance primary healthcare: A qualitative study in rural South Africa. Soc Sci Med. 1982;2018(198):139–47.
Kuntalp M, Akar O. A simple and low-cost Internet-based teleconsultation system that could effectively solve the health care access problems in underserved areas of developing countries. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2004;75(2):117–26.
Price M, Yuen EK, Goetter EM, Herbert JD, Forman EM, Acierno R, Ruggiero KJ. mHealth: a mechanism to deliver more accessible, more effective mental health care. Clin Psychol Psychother. 2014;21(5):427–36.
Bashshur RL, Shannon GW, Krupinski EA, Grigsby J, Kvedar JC, Weinstein RS, Sanders JH, Rheuban KS, Nesbitt TS, Alverson DC, et al. National telemedicine initiatives: essential to healthcare reform. Telemed J E Health. 2009;15(6):600–10.
Norton SA, Burdick AE, Phillips CM, Berman B. Teledermatology and underserved populations. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133(2):197–200.
Raza T, Joshi M, Schapira RM, Agha Z. Pulmonary telemedicine–a model to access the subspecialist services in underserved rural areas. Int J Med Informatics. 2009;78(1):53–9.
Shouneez YH. Smartphone hearing screening in mHealth assisted community-based primary care. UPSpace Institutional Repository, Department of Liberary Service. Dissertation (MCommPath)–University of Pretoria. 2016. Available at http://hdl.handle.net/2263/53477. Accessed 17 Mar 2022.
Marcin JP, Ellis J, Mawis R, Nagrampa E, Nesbitt TS, Dimand RJ. Using telemedicine to provide pediatric subspecialty care to children with special health care needs in an underserved rural community. Pediatrics. 2004;113(1 Pt 1):1–6.
Olu O, Muneene D, Bataringaya JE, Nahimana M-R, Ba H, Turgeon Y, Karamagi HC, Dovlo D. How can digital health technologies contribute to sustainable attainment of universal health coverage in Africa? A perspective. Front Public Health. 2019;7:341.
Ryan MH, Yoder J, Flores SK, Soh J, Vanderbilt AA. Using health information technology to reach patients in underserved communities: A pilot study to help close the gap with health disparities. Global J Health Sci. 2016;8(6):86.
Buckwalter KC, Davis LL, Wakefield BJ, Kienzle MG, Murray MA. Telehealth for elders and their caregivers in rural communities. Fam Community Health. 2002;25(3):31–40.
WHO Regional Committee for Africa. Promoting the role of traditional medicine in health systems: a strategy for the African Region. World Health Organization. Regional Office for Africa. Available at http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/95467..
Mishra SR, Neupane D, Kallestrup P. Integrating complementary and alternative medicine into conventional health care system in developing countries: an example of Amchi. J Evid-Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015;20(1):76–9.
Mbwambo ZH, Mahunnah RL, Kayombo EJ. Traditional health practitioner and the scientist: bridging the gap in contemporary health research in Tanzania. Tanzan Health Res Bull. 2007;9(2):115–20.
Poudyal AK, Jimba M, Murakami I, Silwal RC, Wakai S, Kuratsuji T. A traditional healers’ training model in rural Nepal: strengthening their roles in community health. Trop Med Int Health : TM & IH. 2003;8(10):956–60.
Payyappallimana U. Role of Traditional Medicine in Primary Health Care: An Overview of Perspectives and Challenges. Yokohama J Social Sciences. 2009;14(6):723–43.
Kange’ethe SM. Traditional healers as caregivers to HIV/AIDS clients and other terminally challenged persons in Kanye community home-based care programme (CHBC), Botswana. SAHARA J. 2009;6(2):83–91.
Habtom GK. Integrating traditional medical practice with primary healthcare system in Eritrea. J Complement Integr Med. 2015;12(1):71–87.
Ejaz I, Shaikh BT, Rizvi N. NGOs and government partnership for health systems strengthening: a qualitative study presenting viewpoints of government, NGOs and donors in Pakistan. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011;11(1):1–7.
Wu FS. International non-governmental actors in HIV/AIDS prevention in China. Cell Res. 2005;15(11):919–22.
Biermann O, Eckhardt M, Carlfjord S, Falk M, Forsberg BC. Collaboration between non-governmental organizations and public services in health–a qualitative case study from rural Ecuador. Glob Health Action. 2016;9(1):32237.
Mercer A, Khan MH, Daulatuzzaman M, Reid J. Effectiveness of an NGO primary health care programme in rural Bangladesh: evidence from the management information system. Health Policy Plan. 2004;19(4):187–98.
Baqui AH, Rosecrans AM, Williams EK, Agrawal PK, Ahmed S, Darmstadt GL, Kumar V, Kiran U, Panwar D, Ahuja RC. NGO facilitation of a government community-based maternal and neonatal health programme in rural India: improvements in equity. Health Policy Plan. 2008;23(4):234–43.
Ricca J, Kureshy N, LeBan K, Prosnitz D, Ryan L. Community-based intervention packages facilitated by NGOs demonstrate plausible evidence for child mortality impact. Health Policy Plan. 2014;29(2):204–16.
Ahmed N, DeRoeck D, Sadr-Azodi N. Private sector engagement and contributions to immunisation service delivery and coverage in Sudan. BMJ Glob Health. 2019;4(2):e001414.
Edimond BJ. The Contribution of Non-Governmental Organizations in Delivery of Basic Health Services in Partnership with Local Government. Doctoral Dissertation, Uganda Martyrs University. 2014.
Chand S, Patterson J: Faith-Based Models for Improving Maternal and Newborn Health. IMA World Health and ActionAid International USA, 2007 Available at https://imaworldhealthorg/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/faith_based_models_for_improving_maternal_and_newborn_health.pdf
Magezi V. Churchdriven primary health care: Models for an integrated church and community primary health care in Africa (a case study of the Salvation Army in East Africa). HTS Teologiese Studies/ Theological Studies. 2018;74(2):4365.
Villatoro AP, Dixon E, Mays VM. Faith-based organizations and the Affordable Care Act: Reducing Latino mental health care disparities. Psychol Serv. 2016;13(1):92–104.
Levin J. Faith-based initiatives in health promotion: history, challenges, and current partnerships. American journal of health promotion : AJHP. 2014;28(3):139–41.
Green A, Shaw J, Dimmock F, Conn C. A shared mission? Changing relationships between government and church health services in Africa. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2002;17(4):333–53.
Bandy G, Crouch A. Building from common foundations : the World Health Organization and faith-based organizations in primary healthcare. World Health Organization; 2008. Available at https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43884. Accessed 16 Mar 2022.
Zahnd WE, Jenkins WD, Shackelford J, Lobb R, Sanders J, Bailey A. Rural cancer screening and faith community nursing in the era of the Affordable Care Act. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2018;29(1):71–80.
Wagle K. Primary Health Care (PHC): History, Principles, Pillars, Elements & Challenges. Global Health, 2020. Available at https://www.publichealthnotes.com/primary-health-care-phc-history-principles-pillars-elements-challenges/. Accessed 4 June 2022.
Bhatt J, Bathija P. Ensuring access to quality health care in vulnerable communities. Acad Med. 2018;93(9):1271.
Arvey SR, Fernandez ME. Identifying the core elements of effective community health worker programs: a research agenda. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(9):1633–7.
Pennel CL, McLeroy KR, Burdine JN, Matarrita-Cascante D, Wang J. Community health needs assessment: potential for population health improvement. Popul Health Manag. 2016;19(3):178–86.
Chudgar RB, Shirey LA, Sznycer-Taub M, Read R, Pearson RL, Erwin PC. Local health department and academic institution linkages for community health assessment and improvement processes: a national overview and local case study. J Public Health Manag Pract. 2014;20(3):349–55.
Desta FA, Shifa GT, Dagoye DW, Carr C, Van Roosmalen J, Stekelenburg J, Nedi AB, Kols A, Kim YM. Identifying gaps in the practices of rural health extension workers in Ethiopia: a task analysis study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):1–9.
Lehmann U, Sanders D. Community health workers: what do we know about them. The state of the evidence on programmes, activities, costs and impact on health outcomes of using community health workers Geneva: World Health Organization; 2007. Available at https://www.hrhresourcecenter.org/node/1587.html. Accessed 17 Mar 2022.
Chen N, Raghavan M, Albert J, McDaniel A, Otiso L, Kintu R, West M, Jacobstein D. The community health systems reform cycle: strengthening the integration of community health worker programs through an institutional reform perspective. Global Health: Sci Practice. 2021;9(Supplement 1):S32–46.
Roser M, Ortiz-Ospina E: Global rise of education. Our World in Data 2017. Available at https://ourworldindata.org/global-rise-of-education. Accessed on 29 May 2019.
Santelli J, Morreale M, Wigton A, Grason H. School health centers and primary care for adolescents: a review of the literature. J Adolesc Health. 1996;18(5):357–66.
Wade TJ, Mansour ME, Guo JJ, Huentelman T, Line K, Keller KN. Access and utilization patterns of school-based health centers at urban and rural elementary and middle schools. Public Health Reports. 2008;123(6):739–50.
Johnson I, Hunter L, Chestnutt IG. Undergraduate students’ experiences of outreach placements in dental secondary care settings. Eur J Dent Educ. 2012;16(4):213–7.
Ndira S, Ssebadduka D, Niyonzima N, Sewankambo N, Royall J. Tackling malaria, village by village: a report on a concerted information intervention by medical students and the community in Mifumi Eastern Uganda. Afr Health Sci. 2014;14(4):882–8.
Frakes K-a, Brownie S, Davies L, Thomas JB, Miller M-E, Tyack Z. Capricornia Allied Health Partnership (CAHP): a case study of an innovative model of care addressing chronic disease through a regional student-assisted clinic. Aust Health Rev. 2014;38(5):483–6.
Frakes KA, Brownie S, Davies L, Thomas J, Miller ME, Tyack Z. The sociodemographic and health-related characteristics of a regional population with chronic disease at an interprofessional student-assisted clinic in Q ueensland C apricornia A llied H ealth P artnership. Aust J Rural Health. 2013;21(2):97–104.
Frakes K-A, Tyzack Z, Miller M, Davies L, Swanston A, Brownie S. The Capricornia Project: Developing and implementing an interprofessional student-assisted allied health clinic. 2011.
Frakes K-A, Brownie S, Davies L, Thomas J, Miller M-E, Tyack Z. Experiences from an interprofessional student-assisted chronic disease clinic. J Interprof Care. 2014;28(6):573–5.
Schutte T, Tichelaar J, Dekker RS, van Agtmael MA, de Vries TP, Richir MC. Learning in student-run clinics: A systematic review. Med Educ. 2015;49(3):249–63.
Paim J, Travassos C, Almeida C, Bahia L, Macinko J. The Brazilian health system: history, advances, and challenges. The Lancet. 2011;377(9779):1778–97.
Rocha R, Soares RR. Evaluating the impact of community-based health interventions: evidence from Brazil’s Family Health Program. Health Econ. 2010;19(S1):126–58.
Rasella D, Harhay MO, Pamponet ML, Aquino R, Barreto ML. Impact of primary health care on mortality from heart and cerebrovascular diseases in Brazil: a nationwide analysis of longitudinal data. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2014;349:g4014.
Harris M. Brazil’s Family Health Programme: A cost effective success that higher income countries could learn from. BMJ: Br Med J. 2010;341(7784):1171–2.
Starfield B. Is primary care essential? The lancet. 1994;344(8930):1129–33.
Donfouet HPP, Mahieu P-A. Community-based health insurance and social capital: a review. Heal Econ Rev. 2012;2(1):1–5.
Zhang L, Wang H, Wang L, Hsiao W. Social capital and farmer’s willingness-to-join a newly established community-based health insurance in rural China. Health Policy. 2006;76(2):233–42.
Donfouet HPP. Essombè J-RE, Mahieu P-A, Malin E: Social capital and willingness-to-pay for community-based health insurance in rural Cameroon. Global J Health Sci. 2011;3(1):142.
Grunau J. Exploring people’s motivation to join or not to join the community-based health insurance’Sina Passenang’in Sotouboua, Togo. 2013.
Gitahi JW. Innovative Healthcare Financing and Equity through Community Based Health Insurance Schemes (CBHHIS) In Kenya. United States International University-Africa Digital Repository. Available at http://erepo.usiu.ac.ke/11732/3654. Accessed 18 May 2022.
Carrin G, Waelkens MP, Criel B. Community-based health insurance in developing countries: a study of its contribution to the performance of health financing systems. Tropical Med Int Health. 2005;10(8):799–811.
Umeh CA, Feeley FG. Inequitable access to health care by the poor in community-based health insurance programs: a review of studies from low-and middle-income countries. Global Health: Science And Practice. 2017;5(2):299–314.
Odebiyi AI. Western trained nurses’ assessment of the different categories of traditional healers in southwestern Nigeria. Int J Nurs Stud. 1990;27(4):333–42.
Abdullahi AA. Trends and challenges of traditional medicine in Africa. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med : AJTCAM. 2011;8(5 Suppl):115–23.
Taye OR. Yoruba Traditional Medicine and the Challenge of Integration. The J Pan Afr Studies. 2009;3(3):73–90.
Konadu K. Medicine and Anthropology in Twentieth Century Africa: Akan Medicine and Encounters with (Medical) Anthropology. African Studies Quarterly. 2008;10(2 & 3).
Benzie IF, Wachtel-Galor S: Herbal medicine: biomolecular and clinical aspects. 2nd Ed. 2011. Available at https://www.crcpress.com/Herbal-Medicine-Biomolecular-and-Clinical-Aspects-Second-Edition/Benzie-Wachtel-Galor/p/book/9781439807132. Accessed 21 May 2022.
Ejughemre U. Donor support and the impacts on health system strengthening in sub-saharan africa: assessing the evidence through a review of the literature. Am J Public Health Res. 2013;1(7):146–51.
Seppey M, Ridde V, Touré L, Coulibaly A. Donor-funded project’s sustainability assessment: a qualitative case study of a results-based financing pilot in Koulikoro region. Mali Globalization and health. 2017;13(1):1–15.
Shaw RP, Wang H, Kress D, Hovig D. Donor and domestic financing of primary health care in low income countries. Health Systems & Reform. 2015;1(1):72–88.
Gotsadze G, Chikovani I, Sulaberidze L, Gotsadze T, Goguadze K, Tavanxhi N. The challenges of transition from donor-funded programs: results from a theory-driven multi-country comparative case study of programs in Eastern Europe and Central Asia supported by the Global Fund. Global Health: Science and Practice. 2019;7(2):258–72.
Ascroft J, Sweeney R, Samei M, Semos I, Morgan C. Strengthening church and government partnerships for primary health care delivery in Papua New Guinea: Lessons from the international experience. Health policy and health finance knowledge hub Working paper series. 2011(16).
Campbell MK, Hudson MA, Resnicow K, Blakeney N, Paxton A, Baskin M. Church-based health promotion interventions: evidence and lessons learned. Annu Rev Public Health. 2007;28:213–34.
Olivier J, Wodon Q. The role of faith-inspired health care providers in Sub-Saharan Africa and public private partnerships: Strengthening the Evidence for faith-inspired health engagement in Africa, Volume 1. Health, Nutrition and Population (HNP) Discussion Paper Series 76223v1. Available at https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/851911468203673017. Accessed 20 May 2022.
Schumann C, Stroppa A, Moreira-Almeida A. The contribution of faith-based health organisations to public health. Int Psychiatry. 2011;8(3):62–4.
Travel Journals
An art-filled road trip from Chicago to Detroit
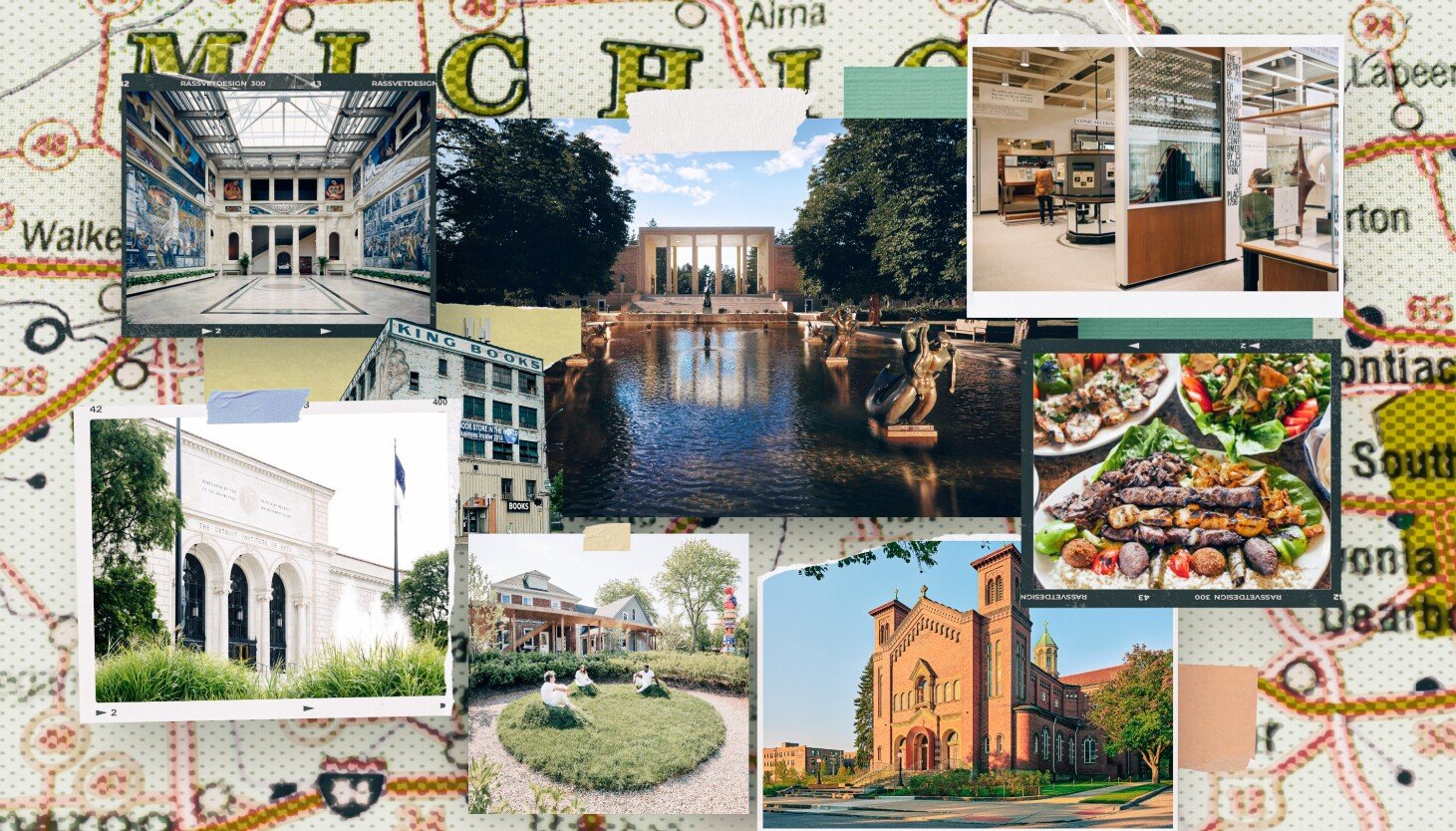

To drive through Detroit is to move through a landscape shaped by both its storied industrial legacy and its long-standing creative community, where generations of artists have turned the city’s factories, urban prairies and waterfront into a living canvas.
The third installment of the WBEZ and Chicago Sun-Times visual art road trip heads east to Detroit and its smaller neighboring cities, where the materials of the past — steel, brick, salvaged wood — aren’t just inspiration but building blocks in a vibrant cultural landscape.
DEARBORN: Arab American Heritage and next-level cashews
Before delving into Detroit, first stop in Dearborn, a suburb that offers a cultural experience rooted in industrial history and Arab American heritage.
The Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation houses iconic objects from American life. “It’s just huge, like the size of an airplane hangar,” said Shelley Selim, the Mort Harris Curator of Automotive, Industrial and Decorative Design at the Detroit Institute of Arts. “There’s a Buckminster Fuller Dymaxion House there, and the Eames ‘Mathematica’ exhibition that they designed for a World’s Fair for IBM.” Next door, Greenfield Village recreates streetscapes from centuries past, with historic homes, steam engines and a glassblowing studio where visitors can watch artists at work.
Arab American communities have been rooted in east Dearborn for more than a century. Many families arrived in the early 20th century to work for Ford and other automakers. In 2023, it became the country’s first city with an Arab American majority.
AlTayeb remains a favorite for Lebanese breakfast platters. The fatteh stands out — layers of toasted pita, chickpeas, warm yogurt, pine nuts and olive oil. Portions are generous; flavors are bold, earthy and bright. For a hearty lunch, try the combo platter at James Beard Award-winning Al Ameer, which includes a generous spread of chicken tawook, lamb kofta, shish kebab, falafel and perfectly fluffed rice.
Before leaving town, Hashem’s Nuts & Coffee Gallery offers a fragrant stop. Shelves are packed with Middle Eastern spices, roasted coffees, and hard-to-find blends like ras el hanout. Selim makes regular trips to the shop where she stocks up on jumbo Brazilian cashews.
DETROIT: A city of space, memory and imagination
The Detroit Institute of Arts (DIA) houses one of the country’s most significant public collections. At its center is the Diego Rivera Court, named after the renowned Mexican painter and muralist who vividly portrayed social inequity, labor struggles and industrialization. “It rewards you every time you look at it,” said Selim. “There’s even a cheat sheet in the tile floor — little carved labels tell you what each panel depicts.” Rivera’s 1932 fresco of the Ford Rouge Plant stretches across four walls and grapples with the tensions between machines, myth, labor and land.
Nearby, “Quilting Time,” a large mosaic by Romare Bearden, pays tribute to communal labor and visual abstraction. “It is just a really stunning representation of community, of women coming together,” Selim said. “And the abstraction of the quilts is just spectacular.”
East of the museum, the Shepherd — a decommissioned Catholic church — has been converted into a contemporary art space by Library Street Collective, a Detroit-based organization known for turning historic buildings into community cultural hubs.
The current Shepherd show, “The Sea and the Sky, and You and I,” centers artists whose work “reflects on histories of landscape.” Among the works are three sculptures by Detroit artist Scott Hocking, who built the pieces from salvaged materials collected at a nearby marina. The artist “considers the cultural memory of the city and the material memory of the city,” said Allison Glenn, a Detroit native who curated the show.
The show, which runs through Aug. 30, also includes work by Midwest sculptor and activist Jordan Weber, whose installation features a spliced GTO Judge — a muscle car originally built by Black assembly line workers — emerging from the floor like a buried relic. The sculpture echoes Weber’s ongoing collaboration with Canfield Consortium, a local nonprofit in the East Canfield neighborhood, which has long grappled with industrial pollution from nearby auto factories. There, Weber installed an air-quality beacon and plans to plant a conifer forest to absorb airborne pollutants.
Public art like Weber’s builds on a long legacy of community-based arts efforts in Detroit. One of the most recognizable is The Heidelberg Project, started in the 1980s by artist Tyree Guyton, who transformed his family’s former home — and eventually two surrounding blocks left in disrepair after the 1967 uprising — into a colorful, ever-evolving wonderland.
For a different kind of spin through history, Submerge is home to the techno label Underground Resistance. Glenn calls it “the world’s first known techno museum.” The space includes a basement record store and rotating tours led by Detroit music legends like Jon Dixon and Cornelius Harris.
Across town, on the city’s West Side, the Dabls Mbad African Bead Museum spans an entire block. “The founder, Olayami Dabls, really appreciated the symbolic and cultural significance of beads within the African and African diasporic communities,” Selim said. “It’s a really cool artist-created environment.”
John K. King Used & Rare Books, located in a former glove factory just west of downtown, feels suspended in time. “Every sale is handwritten down in a ledger,” said Selim of the DIA. Pull-cord lights and floor-to-ceiling stacks make the browsing feel both intimate and endless. “You’ll always find something unique and interesting.”
Round out the day at Paramita Sound, a downtown wine bar and listening room that pairs vinyl sets with high communal tables and natural wine. “Even if you don’t want to talk to anyone,” said Glenn, “you’ll be socializing.”
BLOOMFIELD HILLS: Midcentury icons and palatial grounds
Set on more than 300 acres of landscaped grounds and landmark architecture, Cranbrook Art Museum in Bloomfield Hills beckons as a design destination and a place to wander. “People just explore the grounds for landscape architecture and sculpture,” said Laura Mott, chief curator of the museum. “It’s really just one of the gems of America.”
The current show, “Eventually Everything Connects: Mid-Century Modern Design in the U.S.,” is an ambitious exhibition that revisits the midcentury design canon. “We’ve done a lot of work excavating individuals who are diversifying American modern design,” said Mott. That includes a “textile forest” that hangs from the museum ceiling and walls and features works by such designers as Alexander Girard, Ruth Adler Schnee and Olga Lee. The show is on view through Sept. 21.
Cranbrook’s buildings themselves are also part of the draw. The museum was designed by Eliel Saarinen and opened in 1942. Visitors can also tour the Saarinen House, where Eliel and Loja Saarinen lived while the Cranbrook academy was established, or book a visit to Frank Lloyd Wright’s Smith House, one of Michigan’s best-preserved examples of Wright’s Usonian homes.
Bonus: Where to Stay
For those making a weekend of it, ALEO Detroit offers a low-key, art-forward stay in Detroit’s East Village. Warda Bouguettaya, a James Beard Award–winning chef, runs the breakfast program, and the on-site bar Father Forgive Me opens in the afternoon. “The balcony is right above the bar,” said Glenn. “It’s like your backyard, but with better lighting.” And funky, orange wine.
Or try The Siren Hotel, which offers a gilded, atmospheric experience. Set in a former 1920s high-rise, the chic design leans maximalist: velvet upholstery, terrazzo floors and heavy drapery.
Elly Fishman is a journalist and author whose work explores immigration, incarceration and American culture, including the arts. Her writing has appeared in the New York Times, GQ, Rolling Stone, WBEZ Chicago, among others. She is currently working on her second book, forthcoming from HarperCollins.
Travel Journals
Sophie Morgan to host new series on California’s best road trips
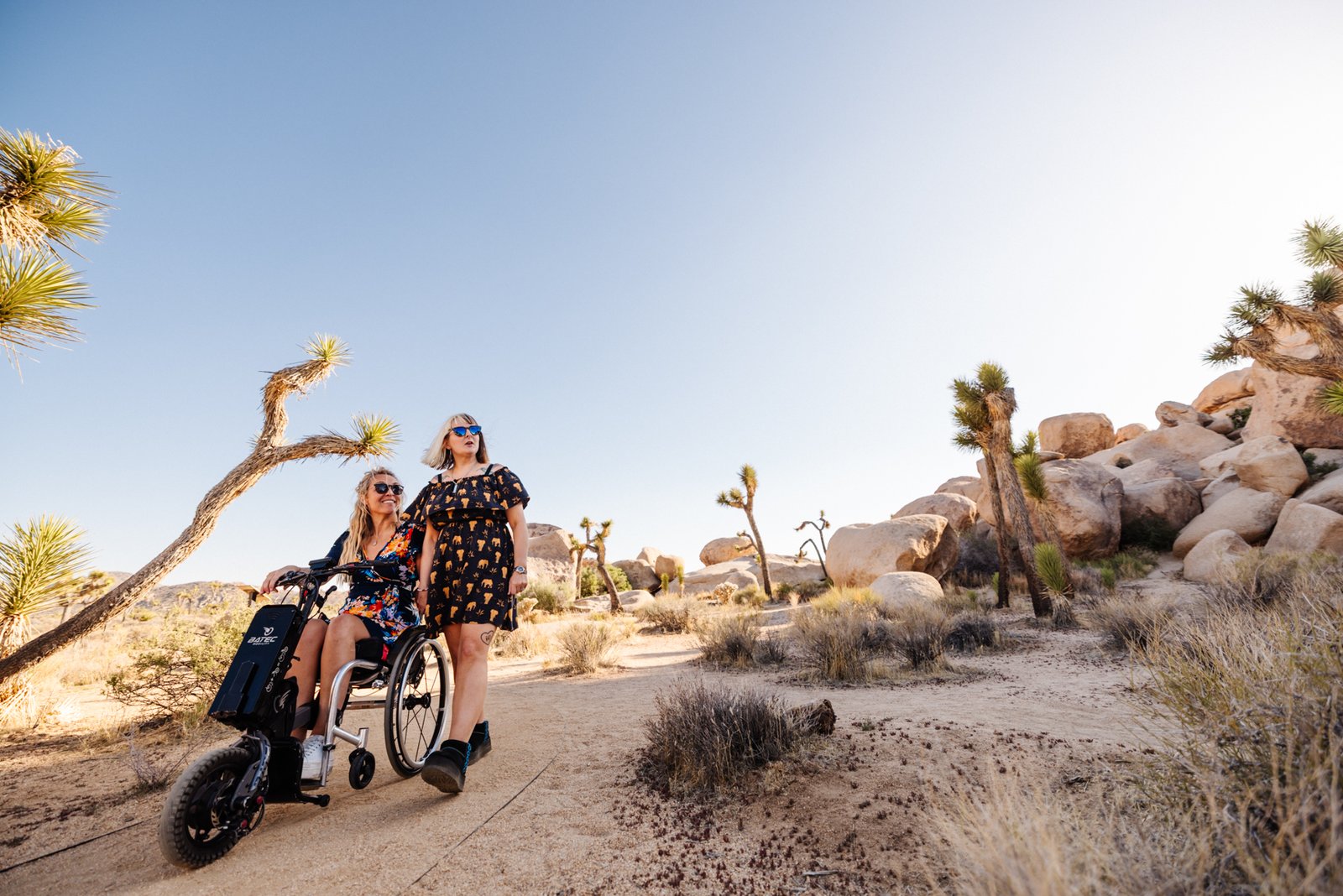

The USA is a destination that’s made for road trips – the only problem is deciding where to start. But if California was on your shortlist, we think this new series might just convince you to book those flights.
Disability advocate and Wanderlust contributing editor Sophie Morgan has just unveiled Joy Diversion, a three-part series exploring the Sunshine State’s epic road adventures.
In the series, Morgan showcases three distinct itineraries: City to Desert, which takes in Greater Palm Springs, Joshua Tree National Park and the Western-themed Pioneertown; Mountains to Lakes, which follows Highway 395 from Mammoth Lakes to the shores of South Lake Tahoe; and Vineyards to the Coast, which puts the spotlight on the wine country of the Santa Ynez Valley, followed by Santa Barbara.
Episodes can be found on Visit California’s YouTube channel, with two episodes already live. The third will premier on 11 August.
Morgan brings a personal perspective to the series, having moved to LA last year.
“I truly believe that California is one of the most accessible destinations in the world, which is why I’m so excited to partner with Visit California on this epic road trip series,” Morgan said.
“Since moving to LA, I’ve spent so much time exploring the state’s hidden corners with friends, old and new and I’ve been blown away by the diversity of the state. Joy Diversion is a love letter to those journeys. I hope it inspires people, of all abilities, to take their own road trip and feel that same joy, freedom and sense of belonging.”
In Joy Diversion, Morgan is joined by friends including broadcaster, author and LGBTQ+ advocate Riyadh Khalaf and Emmy-award winning TV presenter Emily Evans.
The new series will also feature on Visit California’s Accessibility Hub, which provides information for travellers with disabilities including wheelchair-friendly accommodation and sensory-friendly destinations.
More information: visitcalifornia.com/things-to-do/accessible-travel
Read next: Welcome to California
Travel Journals
Why are Titans spending next 2 weeks road tripping? Brian Callahan, players explain value

It’s still summer, but this sure won’t be a summer vacation.
The Tennessee Titans will spend parts of the next 10 days on the road, logging a total of nine nights in Tampa and Atlanta on a preseason road trip for joint practices and preseason games against the Tampa Bay Buccaneers and Atlanta Falcons. It won’t be the busiest slate; the Titans will only practice three times with two games in between, meaning there will be four off days. But it’ll be a stretch spent together, and, crucially to coach Brian Callahan, it’ll be a stretch where opponents will be able to start forming their opinions about the Titans.
Advertisement
“One of the things I’m really looking for is what do those teams say about us when we leave?” Callahan asks rhetorically. “What do they say about how we played, the intensity we practiced with? Those are all things we get to go make an imprint of what our team can be this year.”
ROSTER TALK: Tennessee Titans roster projection: 5 tweaks to 53-man depth chart after training camp Week 2
Callahan envisions this road trip as an opportunity for his players and coaches to get closer, continuing the ongoing trend of Callahan emphasizing connection and togetherness as team-building tacts. It’s also an opportunity to get ready for the long road trips the Titans will have to endure in the fall; the Titans travel to Phoenix, Denver, Las Vegas and San Francisco this season, with the Raiders and Cardinals trips coming in back-to-back weeks.
The players seem to be bought into the idea. Receiver Calvin Ridley says the trip will go a long way toward bringing the team together. Rookie tight end Gunnar Helm says he’s looking forward to getting closer with his teammates. And offensive tackle Dan Moore Jr., in his first year with the Titans, plans to take advantage of the closeness.
Advertisement
“I do think it’s a great time for us to bond us a team,” Moore said. “Spend some time on the road. Get to know each other a little bit better, spend a lot more time with each other and just come together.”
Practicing with the Buccaneers presents a long list of challenges. Coach Todd Bowles’ defense blitzes at one of the highest rates in the league, which should test quarterback Cam Ward and the offense’s readiness. Quarterback Baker Mayfield and the Bucs’ talented receiving corps, led by Mike Evans, will be a huge test for the secondary. And then there’s the Florida heat. The forecast calls for mid-90s temperatures and extreme heat with a “real feel” of 104 degrees by the time practice is going to be ending.
When asked if he has any advice for enduring the Florida summer heat, cornerback and Florida native Jarvis Brownlee Jr. said to keep hydrated. And then he repeated his advice four more times.
Another underrated element is these joint practices, and preseason games, will be the Titans’ first opportunities to experience unfriendly environments. Having enemy fans around isn’t high on the list of reasons to go on these trips, but it’s a factor.
Advertisement
“It’s gonna be us against everybody for the next 10 days,” Helm says.
Nick Suss is the Titans beat writer for The Tennessean. Contact Nick at nsuss@gannett.com. Follow Nick on X @nicksuss. Subscribe to the Talkin’ Titans newsletter for updates sent directly to your inbox.
This article originally appeared on Nashville Tennessean: Why Tennessee Titans are spending 10 days away from Nashville
-

 Brand Stories2 weeks ago
Brand Stories2 weeks agoBloom Hotels: A Modern Vision of Hospitality Redefining Travel
-

 Brand Stories2 weeks ago
Brand Stories2 weeks agoCheQin.ai sets a new standard for hotel booking with its AI capabilities: empowering travellers to bargain, choose the best, and book with clarity.
-

 Destinations & Things To Do3 weeks ago
Destinations & Things To Do3 weeks agoUntouched Destinations: Stunning Hidden Gems You Must Visit
-

 Destinations & Things To Do2 weeks ago
Destinations & Things To Do2 weeks agoThis Hidden Beach in India Glows at Night-But Only in One Secret Season
-

 AI in Travel3 weeks ago
AI in Travel3 weeks agoAI Travel Revolution: Must-Have Guide to the Best Experience
-

 Brand Stories1 month ago
Brand Stories1 month agoVoice AI Startup ElevenLabs Plans to Add Hubs Around the World
-

 Brand Stories4 weeks ago
Brand Stories4 weeks agoHow Elon Musk’s rogue Grok chatbot became a cautionary AI tale
-

 Brand Stories2 weeks ago
Brand Stories2 weeks agoContactless Hospitality: Why Remote Management Technology Is Key to Seamless Guest Experiences
-

 Asia Travel Pulse1 month ago
Asia Travel Pulse1 month agoLooking For Adventure In Asia? Here Are 7 Epic Destinations You Need To Experience At Least Once – Zee News
-

 AI in Travel1 month ago
AI in Travel1 month ago‘Will AI take my job?’ A trip to a Beijing fortune-telling bar to see what lies ahead | China
